Neodymium Magnet Grades: Unveiling the Spectrum of Strength

Neodymium Magnets
Listen to this Article
Reading Magnet Grades
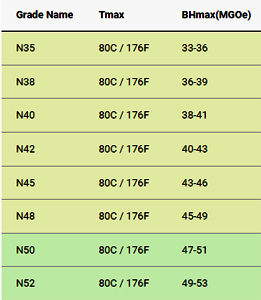
The various grades for Neodymium magnets are each denoted by letters and a number. This combination of letters and numbers signifies the strength of a magnet and its temperature resistance. The strength of the magnet is indicated by the number, which tells the BHmax of the magnet. BHmax is simply a representation of magnetic flux or magnetic strength. For example, an N35 magnet will have a BHmax or strength of around 35. The image to the side shows some of the basic grades of Neodymium along with their temperature maximums and BHmax. As the number in the grade name increases, so does the strength of the magnet. How much increase? Going from an N40 magnet to an N52 magnet will generally result in around a 30% increase in strength.
The letters in the name denote the material being used in the magnet. This material determines the temperature resistance of the magnet or the “Tmax”. A magnet’s Tmax is simply the temperature level at which the magnet can become compromised and start losing strength. There are options for magnetic materials with temperature resistance as high as 446°F.
There are many grades of Neodymium for all types of applications. The most commonly used grades include N35, N40, and N52. For most applications that do not require the magnets to be able to resist high temperatures, these grades will work perfectly. If you are interested in seeing a full chart of all the available grades of Neodymium, you can find one here on our website.
Additional Factors to Consider
Price
When looking for a magnet for a specific application, price can definitely be a determining factor. Generally, the higher the strength of the magnet, the higher the price. How much higher? The price difference between an N40 grade magnet and an N52 grade magnet is generally around 15%. The same is true for temperature resistance. The higher the resistance temperature, the higher the cost. The cost of increasing the temperature resistance of a magnet is generally small at lower temperatures but increases dramatically once extreme temperatures are needed.
Material Brittleness
Another factor to consider when looking at magnet grades is brittleness. As the strength or the temperature resistance of a magnet increases, so does its susceptibility to cracking and chipping. This is because of the different materials being used as well as the tendency of stronger magnets to attract themselves internally. While this increase in weakness is not extreme, it is something to be aware of when choosing a magnet for your specific project.
Conclusion
Understanding magnet grades is a useful skill to possess. Hopefully, this little article has helped you not only gain the necessary knowledge to understand magnet grades but also the confidence needed to make informed decisions about what magnet is best for your project. If you have any questions about grades or what would be suitable for your application, please feel free to contact us at 1-512-678-2940 or visit our website at Amazingmagnets.com.
