Paramagnetic vs Diamagnetic
Listen to this Article
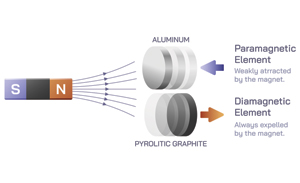
Paramagnetic materials are those that are attracted to an external magnetic field. This is due to the presence of unpaired electrons in their atoms, which align with the magnetic field and create a net magnetic moment in the material. Some common examples of paramagnetic materials include aluminum, platinum, and oxygen.
On the other hand, diamagnetic materials are those that are repelled by an external magnetic field. This is due to the absence of unpaired electrons in their atoms, which means that there is no net magnetic moment in the material. Some common examples of diamagnetic materials include copper, silver, and gold.
It is important to note that both paramagnetism and diamagnetism are relatively weak forms of magnetism compared to ferromagnetism, which is observed in materials like iron and nickel. However, the distinction between paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials is still important in understanding the behavior of different types of materials in the presence of a magnetic field.
Understanding the properties of paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials is crucial in various fields such as chemistry, physics, and materials science. In chemistry, it can be used to explain the magnetic properties of molecules and their reactivity. In physics, it is used to understand the behavior of atoms and subatomic particles. In materials science, it is used to design and develop new materials with specific magnetic properties.
